No-Code and OpenAI Platform: A Magic Combination?
Bridging AI’s Gaps: Testing No-Code Solutions for Smarter, More Autonomous LLMs
Large Language Models (LLMs) have evolved rapidly, reshaping industries with their ability to write, code, and automate workflows. Their transformative potential is undeniable, but to function effectively as agents, LLMs need two critical capabilities: the ability to ingest+persist data autonomously across sessions; and the ability to pull in and manipulate data from various sources using authenticated sources.
Many companies, including OpenAI, are actively working on solutions to bridge these gaps. But I wondered—could I create a practical solution for a specific business need using existing no-code tools?
Experimenting with No-Code: Make.com & Fireflies.ai
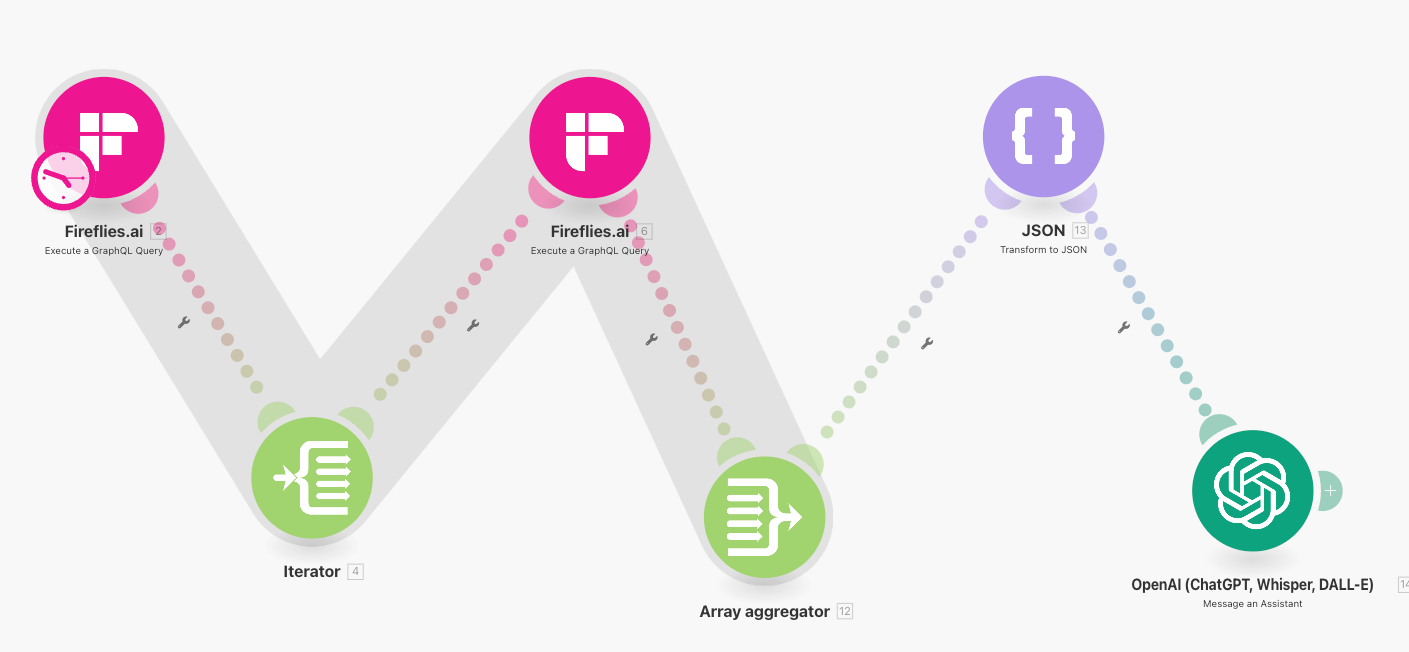
I’ve been testing "Make" (make.com), a no-code integration tool similar to Zapier but with more robust workflows and logic. Additionally, I’ve been an avid user of "Fireflies.ai," an AI-driven meeting notetaker and summarizer.
At work, I used to rely on an admin to provide daily summaries and task reminders. The admin, a few hours ahead in time, would send a structured update that helped me focus my day. Could I replicate this workflow using no-code tools and OpenAI’s platform?
Building a Custom AI-Powered Workflow
I developed multiple automated workflows:
A system that summarizes my daily schedule
A process that extracts action items from past meeting summaries
An OpenAI "Assistant" with a quasi-persistent "thread" for contextual continuity
A notifications module to send out daily notices, and also send responses to those emails back to my GPT assistant.
One major advantage of OpenAI’s Assistants feature is its ability to recall and synthesize information across queries within a thread. By integrating it into my workflow, I could build a more intelligent personal assistant that acted on structured, historical data.
The Results: A Promising Start
The solution worked well but had some quirks. GPT struggled with date/time recognition and time zone adjustments (Claude performed better here). I also had to refine Fireflies’ GraphQL schema integration and manually define contextual parameters to ensure GPT associated the right action items with the correct projects and clients. After around 10 hours of building and iterating, I had a functional, useful solution.
Key Takeaways
ChatGPT Platform’s Assistants API is powerful. There are likely other frameworks that could achieve similar results, but the combination of threaded context and memory storage made it particularly effective.
Cost management is important. Like other LLM API solutions, OpenAI’s model charges per use. Keeping an eye on spend is essential, especially as workflows become more complex. I found GPT-4o-mini sufficient for my use case, with total costs in the low single-digit dollars—scalable, but worth monitoring.
Make.com is great but has limitations. Its support for webhooks and APIs allows for extensibility, but for more advanced needs, I’d consider integrating Lambda or Replit-based functions. However, its "Scenario" model is intuitive and powerful once understood.
Personalized automation can be a game-changer. I now receive structured daily focus emails, and my next step is to push notifications to WhatsApp for even greater usability.
An email gateway (with proper security controls) is a very handy way to access an assistant thread. You can distribute access to multiple people and respond directly to output from an assistant's message. Slack or Whatsapp would work nicely for this as well, both are well supported by Make.
The Future of No-Code AI Integration
This experiment underscored the immense potential of no-code tools when combined with OpenAI’s ecosystem. As AI agents become more autonomous and integration capabilities expand, I foresee a future where complex, personalized automation is accessible to non-technical users, further democratizing AI-driven productivity.



