Around the Horn: AI Development's Big Week
I was going to use "Pivotal", but really every week is pivotal at this point.
The last seven days delivered a series of developments that clarify where AI development is headed. Google's math breakthrough, China's hardware milestone, and Claude Code's meltdown tell a story about capability acceleration meeting economic reality. Here's what happened and why it matters.
Google hits mathematical gold
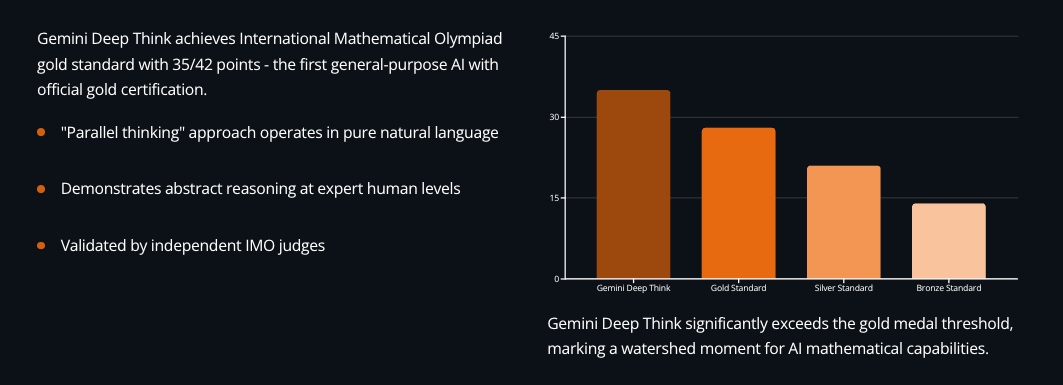
Google DeepMind announced that Gemini Deep Think achieved gold medal standard at the International Mathematical Olympiad, scoring 35 out of 42 points while solving 5 of 6 problems within competition time limits. This isn't just any benchmark - it's the first time a general-purpose AI system has earned official gold certification at the world's premier mathematics competition.
The technical approach centers on what Google calls "parallel thinking" - the system explores multiple solution paths simultaneously before synthesizing answers. Unlike last year's systems that required manual translation to formal languages, Gemini Deep Think operates entirely in natural language, producing rigorous mathematical proofs directly from problem descriptions.
Prof. Dr. Gregor Dolinar, IMO President, confirmed: "Their solutions were astonishing in many respects. IMO graders found them to be clear, precise and most of them easy to follow." The system matched performance of human gold medalists - only 67 of 630 contestants achieved this level.
What makes this significant: we're seeing AI systems handle abstract reasoning at expert human levels, not just pattern matching from training data. The implications for software architecture and mathematical modeling are substantial.
China's hardware independence moment
China launched its first competitive 6nm GPU through Lisuan Technology, with G100-based graphics cards achieving performance comparable to NVIDIA's RTX 4060. The breakthrough represents genuine progress toward semiconductor self-sufficiency despite ongoing U.S. export restrictions.
The numbers tell the story: the Lisuan 7G106 scored 111,290 points on Geekbench OpenCL - 10% faster than RTX 4060, while the AI-focused 7G105 variant delivers up to 24 TFLOPs of FP32 compute performance. Mass production begins September 2025.
This matters for AI development because it demonstrates the partial effectiveness of export controls. China's success with limited resources suggests the global AI hardware market's NVIDIA dominance faces potential disruption. For organizations building AI systems, it signals diversifying supply chains may become both possible and necessary.
Alibaba challenges Western AI leadership
Alibaba's Qwen3-Coder launched with performance approaching Claude Sonnet 4 levels while maintaining 100% open-source availability. The flagship model features 480 billion total parameters with 35 billion active per forward pass, supporting a 256K token context window extendable to 1 million tokens.
On SWE-bench, the model achieved 69.6% resolution rate compared to Claude Sonnet 4's 70.4% - within one percentage point of the proprietary leader. Industry observers noted the significance of China achieving near-parity with Western models while offering unrestricted commercial use through Apache 2.0 licensing.
The model's specifications verify through official documentation: training on 7.5 trillion tokens with 70% code ratio, support for 358 programming languages, and deployment options from local installation to API access. Downloads of Qwen-based coding models surpassed 20 million globally, with integration partnerships emerging across development tool ecosystems.
Claude Code subagents transform development workflows
Anthropic launched Claude Code Subagents between July 23-26, addressing fundamental limitations in AI-assisted development through specialized, context-aware assistants. The feature enables developers to create AI subagents with independent context windows and customized capabilities, solving the "context pollution" problem that has limited complex development workflows.
Subagents operate as Markdown files with YAML frontmatter, stored at user or project levels for team sharing. Each maintains a separate context window preventing interference, with configurable tool access and custom system prompts. Anthropic's internal teams report 50-75% time savings across 10+ departments.
Early adopters highlight significant productivity gains, with implementation patterns emerging around quality control loops and specialized task delegation. I've forked my own multiagent framework to use Claude's agent model - claude-mpm - and the results are promising. I'll write more about that later this week.
While token consumption increases 3-4x with multiple active subagents, the productivity benefits position this as a differentiating feature against competitors Cursor and Windsurf.
MCP ecosystem reaches enterprise scale
The Model Context Protocol ecosystem reached critical mass with over 3,000 MCP servers published and support for 700+ services. Microsoft moved MCP integration to general availability, while AWS announced official MCP servers for Lambda, ECS, and EKS services.
Block (Square) reported 50-75% time savings from company-wide MCP deployment, with thousands of employees using MCP-powered tools daily. The protocol's growth from 1,000 servers in February to 4,405 by March demonstrates adoption velocity. New community servers for Selenium, Discord, and blockchain integration showcase expanding use cases beyond traditional development tools.
The roadmap prioritizes asynchronous operations, centralized registry for server discovery, and multimodality support. Industry consensus positions MCP as complementary to Google's Agent2Agent protocol, with MCP dominating agent-to-tool communication while A2A handles agent-to-agent coordination.
GPT-5's imminent launch intensifies competition
Multiple credible sources reported OpenAI plans to launch GPT-5 in early August 2025, with The Verge breaking the original story cited by Axios, Yahoo Finance, and other outlets. Sam Altman confirmed "soon" on July 19, later demonstrating GPT-5 capabilities on Theo Von's podcast saying "this is GPT-5, and it answered it perfectly."
Technical evidence includes BleepingComputer spotting "gpt-5-reasoning-alpha-2025-07-13" references in code, suggesting final testing phases. The unified system will integrate o3 reasoning capabilities, traditional LLM features, and multimodal support with an expected 1M+ token context window.
OpenAI researcher Alexander Wei confirmed "GPT-5 is coming" with potential to create an "industry shockwave." The launch timing reflects competitive pressure from xAI's Grok 4 and Chinese models like Kimi K2, with analysts viewing the timeline as credible given observable testing activities and infrastructure preparation.
Silicon Valley's $1.25 billion talent offer
Meta's unprecedented $1.25 billion over four years offer to an unnamed AI researcher was declined, as reported by Abel founder Daniel Francis on July 20. The rejected offer, approximately $312.5 million annually, represents the highest reported AI talent compensation to date - this is literally insane - and signals escalating competition for elite researchers.
The Wall Street Journal previously reported Zuckerberg met with OpenAI's Chief Research Officer Mark Chen in spring 2025, who suggested investing more in talent but declined a "huge offer" himself. Meta's aggressive campaign includes hiring 11 researchers from OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google, with Shengjia Zhao named Chief Scientist of Meta Superintelligence Labs on July 25.
Industry reactions include OpenAI "recalibrating compensation" with $2+ million retention bonuses and equity packages exceeding $20 million. Mark Chen's internal memo expressed feeling "as if someone has broken into our home," while Sam Altman criticized Meta's approach as "somewhat distasteful."
Claude Code crisis highlights sustainability challenges
Claude Code experienced significant performance degradation during July 20-27, with TechCrunch reporting "unexpectedly restrictive usage limits" beginning July 15. Max plan subscribers ($200/month) reported hitting 900-message limits within 30 minutes, with resets every 4-5 hours making workflow planning impossible. I've written about this extensively.
GitHub Issue #3377 documented critical behavioral problems including instruction ignoring, false environmental reporting, and unauthorized decision-making. Users described "complete loss of trust in agent reliability," with professional developers abandoning the platform. A Reddit "Open Letter to Anthropic" detailed how experienced developers building platforms across fintech, gaming, and crypto were forced to switch tools.
Anthropic's limited response acknowledged "some users experiencing slower response times" without comprehensive communication or advance notice of changes. Analysis suggests users were potentially receiving $1,000+ worth of daily API calls on $200 subscriptions, creating unsustainable economics - which I've also written about. The crisis reflects broader industry challenges as multiple AI coding tools face similar sustainability issues.
What this week means
This pivotal week showcased both capability breakthroughs and fundamental industry challenges. Google's mathematical reasoning achievement and Alibaba's open-source coding model demonstrate rapidly advancing capabilities, while China's hardware progress suggests export restrictions may accelerate rather than prevent technological advancement.
The explosive growth of the MCP ecosystem and imminent GPT-5 launch signal continued innovation momentum. But Meta's unprecedented talent offers and Claude Code's sustainability crisis reveal underlying tensions between rapid capability advancement and economic viability.
The pattern emerging: technical capabilities are advancing faster than business models can sustainably support them. As the industry navigates these challenges, the convergence of breakthroughs, talent concentration, and sustainability pressures will likely define AI's trajectory through the remainder of 2025.
That's where we stand after a week that compressed months of typical development into seven days. The acceleration continues, but so do the fundamental questions about who can sustain it. Things aren't slowing down - if anything, they're moving faster.